Joint Pain
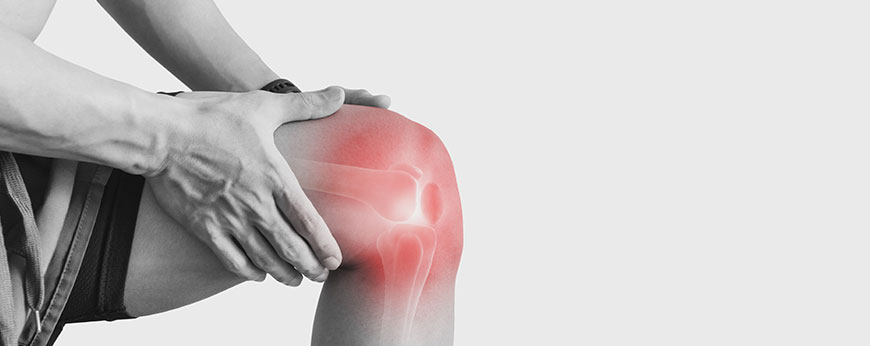
Meaning:
Joint pain refers to discomfort, aches, or soreness in any of the joints in the body, where two or more bones meet. It can be caused by various conditions ranging from acute injuries to chronic diseases like arthritis. Joint pain may affect a single joint or multiple joints and can range from mild discomfort to severe pain that impacts daily activities.
Symptoms:
- Pain, tenderness, or swelling in the affected joint.
- Stiffness, especially in the morning or after inactivity.
- Limited range of motion or difficulty moving the joint.
- Redness, warmth, or visible swelling around the joint.
- In more severe cases, joint deformities or a grinding sensation during movement.
Possible Causes:
- Arthritis: Osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, and psoriatic arthritis are common causes of joint pain.
- Injury or Trauma: Sprains, strains, fractures, or dislocations can lead to joint pain.
- Overuse or Repetitive Motion: Repetitive activities that stress the joints can lead to pain or inflammation (e.g., tendonitis).
- Infections: Joint infections (septic arthritis) caused by bacteria or viruses.
- Gout: A form of arthritis caused by uric acid buildup in the joints, often affecting the big toe.
- Bursitis: Inflammation of the fluid-filled sacs (bursae) that cushion joints.
- Other Conditions: Lupus, fibromyalgia, or Lyme disease can cause joint pain as a symptom.
Care and Treatment:
Self-Care and Lifestyle Modifications:
- Resting the affected joint and avoiding activities that worsen the pain.
- Applying ice or heat packs to reduce swelling and improve circulation.
- Using over-the-counter pain relievers such as acetaminophen or NSAIDs (ibuprofen).
- Elevating the affected joint and supporting it with braces or wraps when necessary.
- Regular low-impact exercises (e.g., swimming, walking) to strengthen muscles around the joint.
Physical Therapy:
- Strengthening exercises to stabilize the joint and improve flexibility.
- Manual therapy to improve joint mobility and reduce pain.
- Stretching techniques to increase range of motion.
Medications:
- Prescription medications, such as disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs) for autoimmune-related joint pain.
- Injections of corticosteroids or hyaluronic acid for pain relief and improved joint function.
Surgical Options:
- In cases of severe joint damage, surgery may be required (e.g., joint replacement or arthroscopy).
- Surgical repair of ligaments or tendons may also be needed if the injury is extensive.
